Creating React and TypeScript apps with Webpack
A more up-to-date post on bundling a React and TypeScript app with Webpack is here.
In this post, we will cover how to use webpack to bundle a React and TypeScript app. We will also include how we can use webpack to provide an awesome experience while developing our app. Our setup will ensure type checking and linting occurs in the webpack process, which will help code quality.

Creating a basic project
Let’s create the following folders in a root folder of our choice:
build: This is where all the artifacts from the build output will be. This will also hold the HTML page that the React app will be injected into.src: This will hold our source code.
Note that a node_modules folder will also be created as we start to install the project’s dependencies.
In the root of the project, add the following package.json file:
{ "name": "my-app", "version": "0.0.1"}This file will automatically update with our project dependencies as we install them throughout this post.
Let’s also add the following index.html file into the build folder:
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="root"></div> <script src="bundle.js"></script> </body></html>Our React app will be injected into the root div element. All the app’s JavaScript code will eventually be bundled together into a file called bundle.js next to index.html in the build folder.
Adding React and TypeScript
Add the following commands in a Terminal to install React, TypeScript and the React types:
npm install react react-domnpm install --save-dev typescriptnpm install --save-dev @types/react @types/react-domTypeScript is configured with a file called tsconfig.json. Let’s create this file in the root of our project with the following content:
{ "compilerOptions": { "lib": ["dom", "dom.iterable", "esnext"], "allowJs": true, "allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true, "skipLibCheck": true, "esModuleInterop": true, "strict": true, "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, "moduleResolution": "node", "resolveJsonModule": true, "isolatedModules": true, "noEmit": true, "jsx": "react" }, "include": ["src"]}We are only going to use TypeScript in our project for type checking. We are going to eventually use Babel to do the code transpilation. So, the compiler options in our tsconfig.json are focused on type checking, not code transpilation.
Here’s an explanation of the settings we have used:
lib: The standard typing to be included in the type checking process. In our case, we have chosen to use the types for the browsers DOM as well as the latest version of ECMAScript.allowJs: Whether to allow JavaScript files to be compiled.allowSyntheticDefaultImports: This allows default imports from modules with no default export in the type checking process.skipLibCheck: Whether to skip type checking of all the type declaration files (*.d.ts).esModuleInterop: This enables compatibility with Babel.strict: This sets the level of type checking to very high. When this istrue, the project is said to be running in strict mode.forceConsistentCasingInFileNames: Ensures that the casing of referenced file names is consistent during the type checking process.moduleResolution: How module dependencies get resolved, which is node for our project.resolveJsonModule: This allows modules to be in.jsonfiles which are useful for configuration files.noEmit: Whether to suppress TypeScript generating code during the compilation process. This istruein our project because Babel will be generating the JavaScript code.jsx: Whether to support JSX in.tsxfiles.include: These are the files and folders for TypeScript to check. In our project, we have specified all the files in thesrcfolder.
Adding a root React component
Let’s create a simple React component in a index.tsx file in the src folder. This will eventually be displayed in index.html.
import React from "react";import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
const App = () => ( <h1>My React and TypeScript App!</h1>);
ReactDOM.render( <App />, document.getElementById("root"));Adding Babel
Our project is going to use Babel to convert our React and TypeScript code to JavaScript. Let’s install Babel with the necessary plugins as a development dependency:
npm install --save-dev @babel/core @babel/preset-env @babel/preset-react @babel/preset-typescript @babel/plugin-transform-runtime @babel/runtimeHere’s an explanation of the packages we have just installed:
@babel/core: As the name suggests, this is the core Babel library.@babel/preset-env: This is a collection of plugins that allow us to use the latest JavaScript features but still target browsers that don’t support them.@babel/preset-react: This is a collection of plugins that enable Babel to transform React code into JavaScript.@babel/preset-typescript: This is a plugin that enables Babel to transform TypeScript code into JavaScript.@babel/plugin-transform-runtimeand@babel/runtime: These are plugins that allow us to use theasyncandawaitJavaScript features.
Configuring Babel
Babel is configured in a file called .babelrc. Let’s create this file in the root of our project with the following content:
{ "presets": [ "@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react", "@babel/preset-typescript" ], "plugins": [ [ "@babel/plugin-transform-runtime", { "regenerator": true } ] ]}This configuration tells Babel to use the plugins we have installed.
Adding linting
We are going to use ESLint in our project. ESLint can help us find problematic coding patterns or code that doesn’t adhere to specific style guidelines.
So, let’s install ESLint along with the plugins we are going to need as development dependencies:
npm install --save-dev eslint eslint-plugin-react eslint-plugin-react-hooks @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-pluginBelow is an explanation of the packages that we just installed:
eslint: This is the core ESLint library.eslint-plugin-react: This contains some standard linting rules for React code.eslint-plugin-react-hooks: This includes some linting rules for React hooks code.@typescript-eslint/parser: This allows TypeScript code to be linted.@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin: This contains some standard linting rules for TypeScript code.
ESLint can be configured in a .eslintrc.json file in the project root.
Let’s create the configuration file containing the following:
{ "parser": "@typescript-eslint/parser", "parserOptions": { "ecmaVersion": 2018, "sourceType": "module" }, "plugins": [ "@typescript-eslint", "react-hooks" ], "extends": [ "plugin:react/recommended", "plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended" ], "rules": { "react-hooks/rules-of-hooks": "error", "react-hooks/exhaustive-deps": "warn", "react/prop-types": "off" }, "settings": { "react": { "pragma": "React", "version": "detect" } }}So, we have configured ESLint to use the TypeScript parser, and the standard React and TypeScript rules as a base set of rules. We’ve explicitly added the two React hooks rules and suppressed the react/prop-types rule because prop types aren’t relevant in React with TypeScript projects. We have also told ESLint to detect the version of React we are using.
Adding webpack
Webpack is a popular tool that we can use to bundle all our JavaScript code into the bundle.js file our index.html expects. Let’s install the core webpack library as well as its command-line interface:
npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli @types/webpackWebpack has a web server that we will use during development. Let’s install this:
npm install --save-dev webpack-dev-server @types/webpack-dev-serverWe need a webpack plugin, babel-loader, to allow Babel to transpile the React and TypeScript code into JavaScript. Let’s install this:
npm install --save-dev babel-loaderThe Webpack configuration file is JavaScript based as standard. However, we can use TypeScript if we install a package called ts-node. Let’s install this:
npm install --save-dev ts-nodeWebpack is configured using a file called webpack.config.ts. Let’s create this in the project’s root directory with the following content:
import path from "path";import { Configuration } from "webpack";
const config: Configuration = { entry: "./src/index.tsx", module: { rules: [ { test: /\.(ts|js)x?$/, exclude: /node_modules/, use: { loader: "babel-loader", options: { presets: [ "@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react", "@babel/preset-typescript", ], }, }, }, ], }, resolve: { extensions: [".tsx", ".ts", ".js"], }, output: { path: path.resolve(__dirname, "build"), filename: "bundle.js", }, devServer: { static: path.join(__dirname, "build"), compress: true, port: 4000, },};
export default config;Here are the critical bits in this configuration file:
- The
entryfield tells Webpack where to start looking for modules to bundle. In our project, this isindex.tsx. - The
modulefield tells Webpack how different modules will be treated. Our project is telling Webpack to use thebabel-loaderplugin to process files with.js,.ts, and.tsxextensions. - The
resolve.extensionsfield tells Webpack what file types to look for in which order during module resolution. - The
outputfield tells Webpack where to bundle our code. In our project, this is the file calledbundle.jsin thebuildfolder. - The
devServerfield configures the Webpack development server. We are telling it that the root of the web server is thebuildfolder, and to serve files on port4000.
Adding type checking into the webpack process
The Webpack process won’t do any type checking at the moment. We can use a package called fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin to enable the Webpack process to type check the code. This means that Webpack will inform us of any type errors. Let’s install this package:
npm install --save-dev fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin @types/fork-ts-checker-webpack-pluginLet’s add this to webpack.config.ts:
...import ForkTsCheckerWebpackPlugin from 'fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin';
const config: Configuration = { ..., plugins: [ new ForkTsCheckerWebpackPlugin({ async: false, eslint: { files: "./src/**/*", }, }), ],};Here’s an explanation of these ForkTsCheckerWebpackPlugin settings:
async: We have set this tofalseso that Webpack waits for the type checking process to finish before it emits any code.eslint: We have set this to point to the source files so that Webpack informs us of any linting errors.
Adding npm scripts
We will leverage npm scripts to start our app in development mode and build a production version of our app. Let’s add a scripts section to package.json with the following scripts:
..., "scripts": { "start": "webpack serve --open", "build": "webpack --mode production" }, ...Let’s run the following command in a terminal to start the app in development mode:
npm startAfter a few seconds, the Webpack development server will start and our app will be opened in our default browser:

We’ll leave the app running.
Let’s make a change to the heading that is rendered in index.tsx. Let’s reference a variable called today in the heading:
...const App = () => <h1>My React and TypeScript App! {today}</h1>;...Of course, this is an error because we haven’t declared and initialized today anywhere. Webpack will raise this type error in the terminal:
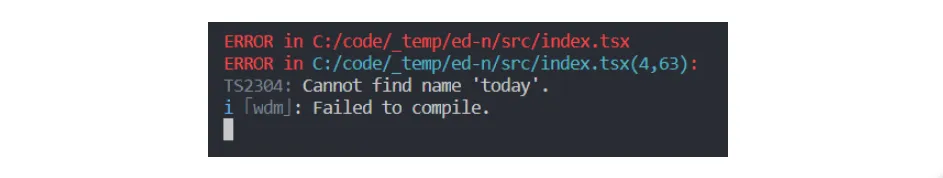
Let’s resolve this now by changing the rendered header to reference something that is valid:
const App = () => ( <h1> My React and TypeScript App!{" "} {new Date().toLocaleDateString()} </h1>);The type errors will vanish, and the running app will have been updated to include today’s date:

Let’s move on now to try the final npm script. This produces a production build of our app. Let’s run the following command in the terminal:
npm run buildAfter a few seconds, a file called bundle.js will appear in the build folder. This file contains all the JavaScript minified code, including code from the React library and React component.
That’s it! Our project is now set up ready for us efficiently develop our React and TypeScript app.
Learn React with TypeScript - 3rd Edition
NewA comprehensive guide to building modern React applications with TypeScript. Learn best practices, advanced patterns, and real-world development techniques.
View on Amazon